Indexing & Abstracting
Full Text
Research ArticleDOI Number : 10.36811/ojnmc.2020.110006Article Views : 2Article Downloads : 1
A study to assess the effectiveness of Rhythmic Breathing exercises on postoperative pain of patient after Abdominal Surgery in selected Hospitals of North Gujarat
Mr. Kaushal Patidar1 and Mr. Kalpesh Patidar2*
1HOD of Medical Surgical Department, JoitibaCollege of Nursing, Bhandu, Dist: Mehsana, India
2Second Year M.SC. Nursing Student, Joitiba College of Nursing, Bhandu, Dist: Mehsana, India
*Corresponding Author: Kalpesh Patidar, Second Year M.SC. Nursing Student, Joitiba College of Nursing, Bhandu, Dist: Mehsana, India, Email: kahilpatel96@gmail.com
Article Information
Aritcle Type: Research Article
Citation: Kaushal Patidar, Kalpesh Patidar. 2019. A study to assess the effectiveness of Rhythmic Breathing exercises on postoperative pain of patient after Abdominal Surgery in selected Hospitals of North Gujarat. Open J Nurs Med Care. 2: 01-07.
Copyright: This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Copyright © 2019; Kaushal Patidar
Publication history:
Received date: 08 October, 2020Accepted date: 19 October, 2020
Published date: 21 October, 2020
Abstract
Background: Deep breathing is one of the best ways to lower stress and pain in the body. This is because when you breathe deeply, it sends a message to your brain to calm down and relax. The brain then sends this message to your body those things that happen when you are stressed, such as increased heart rate, fast breathing and high blood pressure, all decrease as you breathe deeply to relax.
Aims and Objective: To assess the post operative pain of patient after abdominal surgery among experimental and control group. To evaluate the effectiveness of rhythmic breathing exercise on post operative pain after abdominal surgery among experimental group. To determine the post-test score of post operative pain among experimental and control group. To findout the association of post operative pain with selected demographic variable in control and experimental group.
Methods: A quantitative approach using Quasi-experimental research (Nonrandomized control group design.) 40 patients were selected using non probability purposive sampling in selected hospitals of North Gujarat. International numerical pain scale used for subjective pain assessment.
Results: study show that out of 40 subjects in 20 experimental group, group 1(5%) belongs to the age group between 18-27 years, 2(10%) belongs to the age group between 28 -37 years, 5(25%) belongs to the age group between 38-47 years, 9(45%) belongs to the age group between 48-57 years and 3(15%) belongs to the age group of 58 years. and out of 20 In control group 5(25%) belongs to the age group between 18-27 years 3(15%) belongs to the age group between 28-37 years, 4(20%) belongs to the age group between 38-47 years, 4(20%) belongs to the age group between 48-57 years, and 4(20%) belongs to the age group of 58 years and above. In experimental group, majority in pre test19 (95%) reported severe pain, after intervention of rhythmic breathing exercisesin post test 18 (90%) reported mild pain. in control group, majority in pre test 20 (100%) reported severe pain, without intervention of rhythmic breathing exercises in post test reported severe pain 15 (75%). reveals that in experimental group the pre test mean was 7.21 and post test mean was 3.22. The pre test standard deviation was 1.44 and the posttest standard deviation was 1.02. The mean difference was 3.98 and the obtained t-value was 10.18 which are significant at 0.05levels. Hence, the stated hypothesis was accepted. In control group the pre test mean was 8.35 and post test mean was 6.56. The pretest standard deviation was 0.79 and the post test standard deviation was 0.94. The mean difference was 1.78 and the obtained t- value was 6.45 which are not significantat 0.05levels. Hence the stated hypothesis was accepted.
Keywords: Assess effectiveness; Rhythmic breathing exercises; Post operative pain; Abdominal surgery patients
Introduction
Pain is a subjective experience in health and sickness. Most of the medical - surgical conditions are associated with pain. For a hospitalized patient, pain may be an actual problem or patient may anticipate it. Almost all medical - surgical interventions are associated with pain. Patient’s responses to pain will depend on individual perception of the pain influenced by past experience and socio- cultural factors; Surgery in abdomen refers to procedures that involve opening the abdomen and the organs in the abdominal cavity. Abdominal surgery involves tissue destruction followed by a repair or removal of the primary problem [1,2]. Nurses play an important role in the postoperative management of patients, Prevention of complications and speedy recovery of patients for dependency to independency will depend on the nurses’’ role. It is important that the nurses have to understand the pain experience of patients on assessing pain and try to manage pain by adopting measures other than drugs. As seen in the literature, there are various non pharmacological measures to minimize pain. Patents will be able to participate in the postoperative activities only if they are comfortable and are either free from pain or experience minimal pain. Nurses are in a position to try out some of the measures to minimize pain and give a high standard of care to postoperative patients [3].
Need of the study
Post operative breathing exercises are widely important for patient to prevent postoperative respiratory complications. Breathing exercises had highly positive effect on improving quality of recovery among post-operative patients. This study aimed to assess the effect of breathing exercises on quality of recovery among post-operative patients. Setting at zagazig university hospitals. Material and method: a quasi-experimental (pre and posttest design). A purposive sample of total 258 study participants, 129 in experimental and 129 in control group based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data collection questionnaire were prepared with extensive review of previous literatures. Data collection through three include, interviewing questionnaire sheet, post operative quality scale and visual analogue scale of patient postoperative quality assessment scale. Breathing exercise (BE) was taught and practiced by the patient in experimental group and in control group routine postoperative care was followed, postoperative quality rate was significantly different in experimental group were higher than in control group. Post operative breathing exercises improve postoperative quality.significant human suffering as per studies and surveys done over the last half century reporting steadily increasing cases [4]. A study conducted on efficacy of relaxation therapy as an effective nursing intervention for post operative pain relief in patients undergoing abdominal surgery, results:This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with the aim of assessing the efficacy of relaxation techniques for pain relief in patients undergoing abdominal surgery. A total of 12 studies were included in the review and 7 in the meta-analysis. In total, 4 relaxation techniques were utilized in the included studies: Jaw relaxation, Benson's relaxation, progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) and systematic relaxation. Of the 12 included, 10 studies demonstrated statistically significant pain relief in the relaxation group as compared to the controls. The data of 422 patients in the relaxation group and 424 patients in the control group were pooled for a meta-analysis, which indicated that patients undergoing abdominal surgery had significantly greater pain relief following relaxation therapy as compared to the controls [random: standardized mean difference (SMD), -1.15; 95% CI, -2.04 to -0.26; P<0.00001). The overall quality of the studies was not high. On the whole, despite trials demonstrating the benefits of relaxation therapy for immediate pain relief in patient’s post-abdominal surgery, there is lack of high?quality scientific evidence substantiating its routine use. There is a need for more robust randomized control trials (RCTs) utilizing standardized relaxation protocols to provide further evidence on this subject [5-8].
Objective
• To assess the post-operative pain of patient after abdominal surgery among experimental and control group.
• To evaluate the effectiveness of rhythmic breathing exercise on post-operative pain after abdominal surgery among experimental group.
• To determine the post-test score of post-operative pain among experimental and control group.
• To find out the association of post-operative pain with selected demographic variable in control and experimental group.
Hypothisis
• H0(1): There will be no significant difference between pretest and post test score regarding rhythmic breathing exercises in control group at 0.05 level of significance.
• H0(2): There will be no significant difference between pretest and post test score
regarding rhythmic breathing exercises in experimental group at 0.05 level of significance.
• H1(1): There will be a significant difference between pretest and post test score regarding rhythmic breathing exercises in control group at 0.05 level of significance.
• H1(2): There will be a significant difference between pretest and post test score regarding rhythmic breathing exercises in experimental group at 0.05 level of significance.
Material and Methods
A quantitative approach using Quasi-experimental research (Nonrandomized control group design) was used. 40 patients (20 in experimental group and 20 in control group) were selected using nonprobability purposive sampling in GMERS hospital, dharpur, patan, lions hospital and civil Hospital at Mehsana, North Gujarat with usingInternationalnumerical pain scale used for subjective pain assessment.
Results
The demographic variables were analyzed by using descriptive measures (frequency and percentage). The level of pain was analyzed by using descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation). The effectiveness of rhythmic breathing exercises was analyzed by using paired “t” test and independent “t” test. Association between the levels of post-operative abdominal surgery related pain among patient with their selected demographic variables was assessed by chi-square test.
Finding related to demographic data
Among patients with post operative abdominal surgery related pain most of them were between 48-57 years, male gender, have primary education, had 2-4 month of duration of illness, monthly income less than 5000 per month, type of hospital is government, type of surgery majorly other surgeries related to abdominal surgeries.
|
Table 1.1: Frequency and percentage distribution of level of post operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery in experimental group. |
|||||
|
Sl. No. |
Variables |
Pre Test |
Post Test |
||
|
N |
% |
N |
% |
||
|
|
Level of pain |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1. |
a) No pain |
||||
|
2. |
b) Mild pain |
0 |
0 |
18 |
90 |
|
3. |
c) Moderate pain |
1 |
5 |
2 |
10 |
|
4. |
d) Severe pain |
19 |
95 |
0 |
0 |
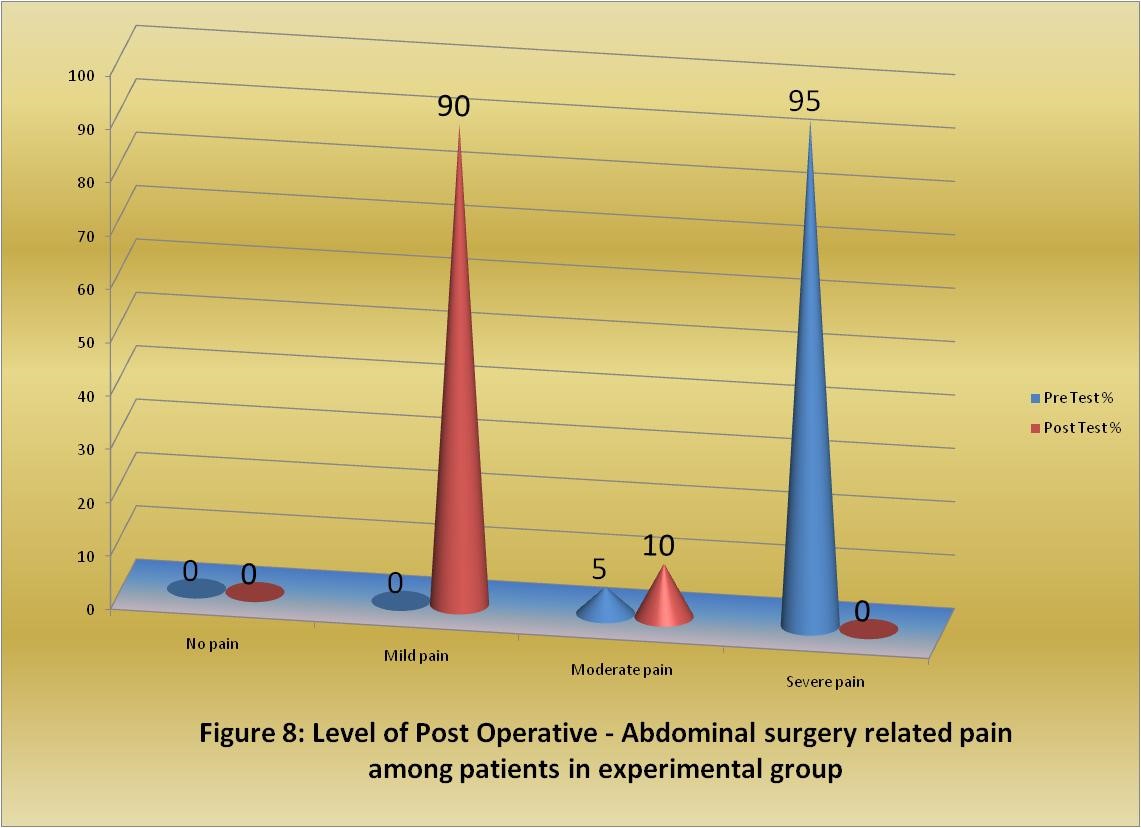
Figure 1: Level of post operative - Abdominal surgery related pain among patients in experimental group.
|
Table 1.2: Frequency and percentage distribution of level of post-operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery in control group. |
|||||
|
Sl. No. |
Variables |
Pre Test |
Post Test |
||
|
n |
% |
N |
% |
||
|
1. |
Level of pain |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
e) No pain |
|||||
|
2. |
f) Mild pain |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
3. |
g) Moderate pain |
0 |
0 |
5 |
25 |
|
4.
|
h) Severe pain |
20 |
100 |
15 |
75 |
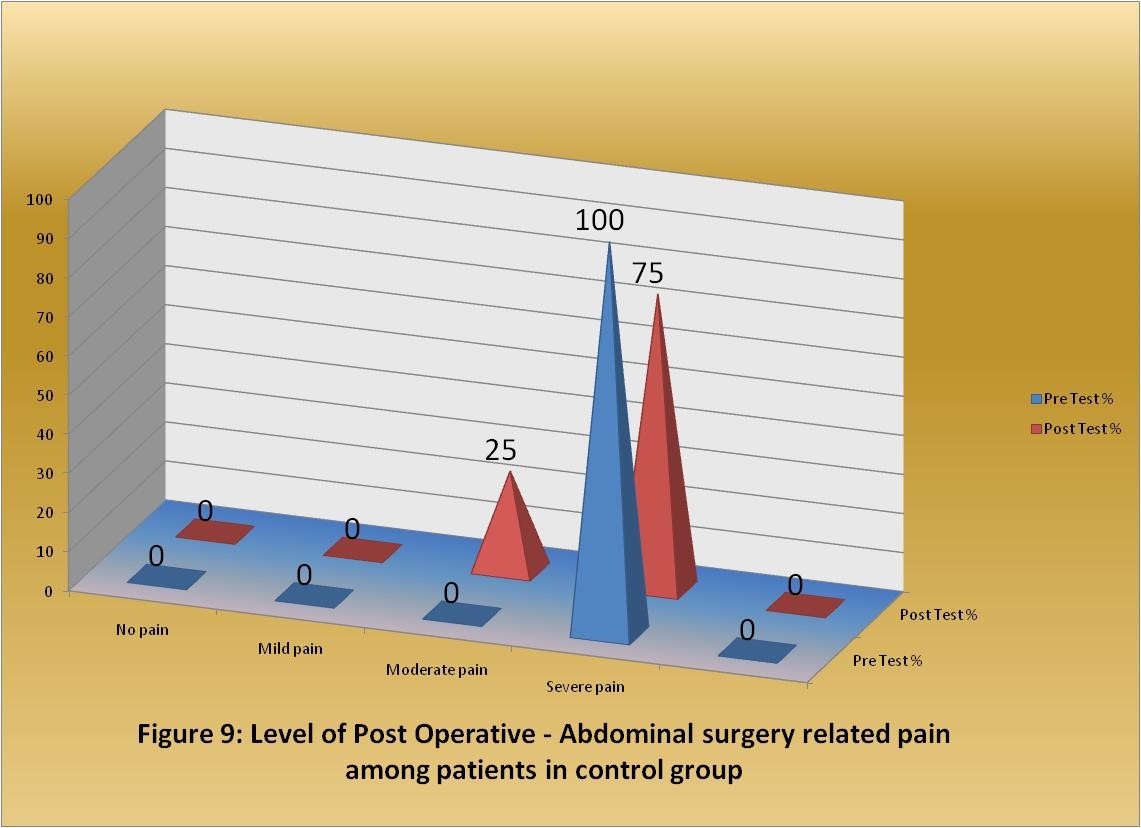
Figure 2: Level of post operative - Abdominal surgery related pain among patients in control group.
Finding related to effectiveness of Rhythmic Breathing Exercises on post operative Abdominal Surgery related pain among Patients:
|
Table 2.1: Mean Standard deviation and t-value of level of post-operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery in experimental group. N=20 |
|||||
|
Sl. No. |
Group |
Mean |
Standard deviation |
Mean difference |
t- value |
|
1. |
Pre Test |
7.21 |
1.44 |
3.98 |
10.18 |
|
2. |
Post Test |
3.22 |
1.02 |
||
|
Table 2.2 Mean Standard deviation and t-value of level of post-operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery in control group. N=20 |
|||||
|
Sl. No. |
Group |
Mean |
Standard deviation |
Mean difference |
t- value |
|
1. |
Control group |
8.35 |
0.79 |
1.78
|
6.45 |
|
Pre Test |
|||||
|
2. |
Post Test |
6.56 |
0.94 |
||
|
Table 2.3: Mean, Standard Deviation, Mean Difference and t - value of post test score of level of post-operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery in Experimental and control group. |
||||||||
|
|
Experimental group |
Control group |
||||||
|
Range |
Mean |
Median |
Standard deviation |
Range |
Mean |
Median |
Standard deviation |
|
|
Pre-test |
6-10 |
7.21 |
9 |
1.44 |
7-10 |
8.35 |
8 |
0.79 |
|
Post- test |
1-4 |
3.22 |
2 |
1.02 |
6-9 |
6.56 |
7 |
0.94 |

Table 2.3: reveals that post test mean score of post-operative surgery related pain in Experimental Group was 3.22 which is lower than the post test mean score of 6.56 in control group. It was inferred that rhythmic breathing exercises was effective in reducing post-operative surgery related pain among patients.
Finding related to association between the level of post operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery with their selected demographic variables.
The association between the level of post-operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery. Based on the fourth objectives used to chi - square test to associate the level of post operative related pain among patient with abdominal surgery with selected demographic variable. The chi square value shows that there is not significant at the 0.05level of significance.
Conclusion
The conclusions drawn from the finding of the study are as follows:
The ‘T’ test is done to find the effect of rhythmic breathing exercises. It revealed that there is highly significant decrease the level of post operative abdominal surgery related pain in experimental group after the administration of intervention. The ‘T’ value is 10.18 (in experimental group) and The ‘T’ value is 06.45 (in control group) and research hypothesis is accepted and null hypothesis is rejected. The pre test and post test mean in experimental group is 7.21% and 3.22% and different is 3.98%. and pre test and post test in control group is 8.35% and 6.56% and difference is 1.78 so decrease the pain score in experimental group after intervention of rhythmic breathing exercises. This indicates that the rhythmic breathing exercises is effective in reducing the post operative abdominal surgery related pain.
References
1. https://www.webmd.com/balance/stress-management/stress-relief-breathing-techniques.
2. Janice L, Hinkle, Kerry H. 2012. Cheever BRUNNER AND SIDDARTH’S TEXT BOOK MEDICAL AND SURGICAL NURSING. 13th Edition, South Asian Edition, Woltes Kluwer Heath Publications. 266-267.
3. According to mr. godwinjebadas, Akshaya College of nursing, tumkur, Karnataka.Study on a study to assess the effectiveness of rhythmic breathing exercise on post - operative pain and selected activities of patients after abdominal surgery in selected hospitals.
4. Effect of Breathing Exercises on Quality of Recovery among Postoperative Patients, International Journal of Studies in Nursing. 2018. 3: 2.
5. Efficacy of relaxation therapy as an effective nursing intervention for post-operative pain relief in patients undergoing abdominal surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis, experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2019. 18: 2909-2916.
6. Basavanthappa BT. 2003. TEXT BOOK OF NURSING RESEARCH. 1st Edition, New Delhi, Jaypee Brothers Medical publishers (pvt) Ltd.
7. Lewis Sharon M, Darkson Shannon Idolia C, Heitkemper MM. 2004. TEXT BOOK OF MEDICAL AND SURGICAL NURSING. 6th Edition, Missouri, Mosby Publication.
8. Nancy Burns, Susan K, Groove. 2005. TEXT BOOK OF THE PRACTICE OF NURSING RESEARCH. 5th Edition, Missouri, Elsevier Saunders publications.




















